About Education in UK
Secondary
In England, public provision of secondary education in an area may consist of a combination of different types of school, the pattern reflecting historical circumstance and the policy adopted by the local authority.
Comprehensive schools largely admit pupils without reference to ability or aptitude and cater for all the children in a neighbourhood, but in some areas they co-exist with other types of schools, for
example grammar schools.
example grammar schools.
Academies, operating in England, are publicly funded independent schools. Academies benefit from greater freedom to help innovate and raise standards. These include freedom from local authority control, the ability to set their own pay and conditions for staff, freedom around the delivery of the curriculum
and the ability to change the lengths of terms and school days. The Academies Programme was first introduced in March 2000 with the objective of replacing poorly performing schools. Academies were established and driven by external sponsors, to achieve a transformation in education performance. The Academies Programme was expanded through legislation in the Academies Act 2010. This enables all maintained primary, secondary and special schools to apply to become an Academy. The early focus is on schools rated outstanding by Ofsted and the first of these new academies opened in September 2010. These schools do not have a sponsor but instead are expected to work with underperforming schools to help raise standards.
In Wales, secondary schools take pupils at 11 years old until statutory school age
and beyond.
Ministerial policy is that transfer should be on the basis of nonacademic criteria, however legally post primary schools can still admit pupils based on academic performance.
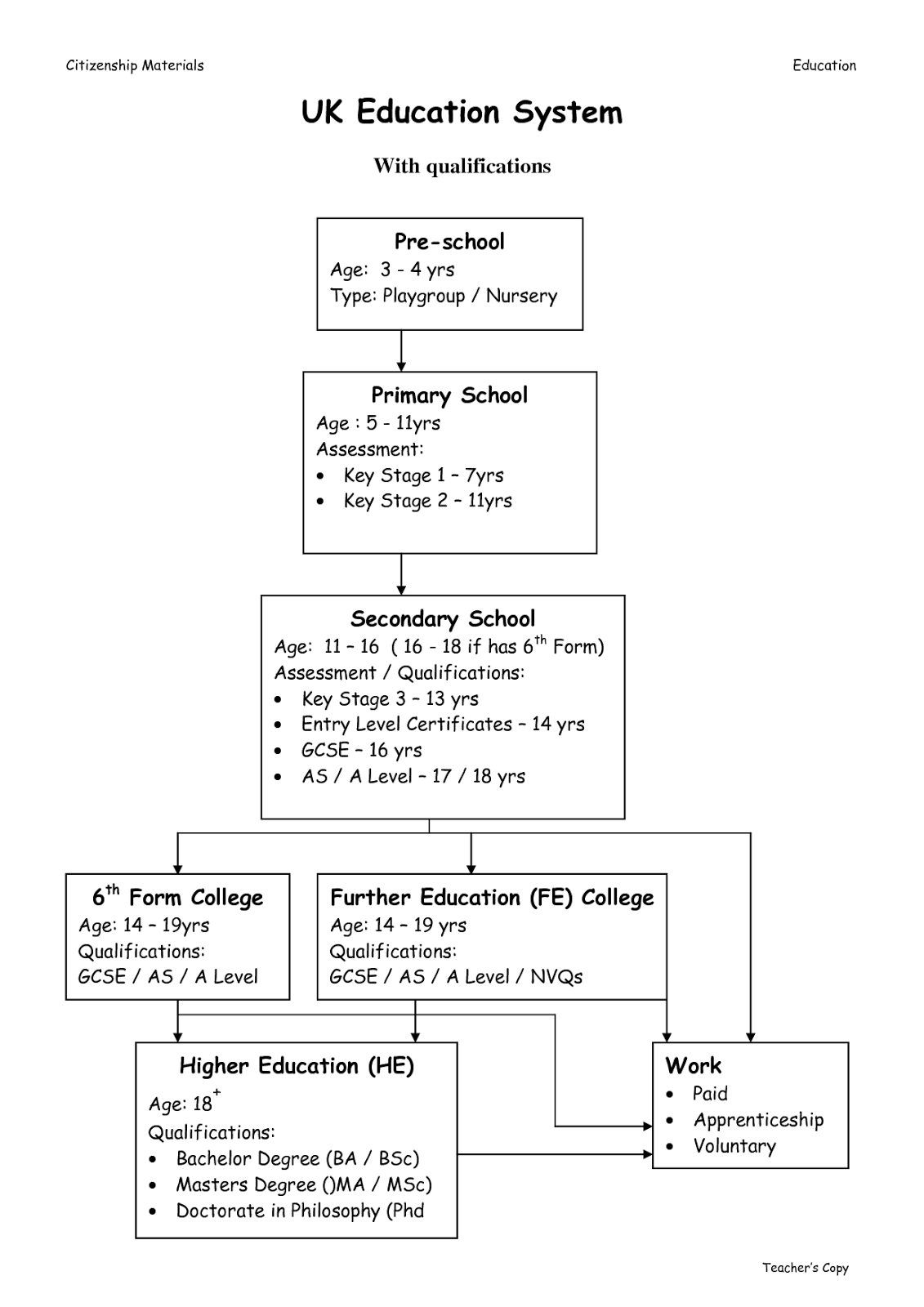
At the end of this stage of education, pupils are normally entered for a range ofexternal examinations. Most frequently, these are GCSE (General Certificate ofSecondary Education) in England, Wales and Northern Ireland and Standard Gradesin Scotland, although a range of other qualifications are available.
The term public school refers to a group of older, more expensive and exclusive private independent schools in the UK, particularly in -england, which cater primarily for children aged between 13 and 18. Together these schools comprise only around 1% of the total number of schoools in the UK. Traditionally, these were boys´boarding schools, although most now allow day pupils and many have turned either partially or fully co-educationally. They emerged from charity schools established to educate por scholars, the term "public" being used to indicated that Access to them was nos restricted on the basis of religión, occupation, or home location, and that they were subject to public management or control in contrast to private schools which were run for the personal profit of the proprietors
and the ability to change the lengths of terms and school days. The Academies Programme was first introduced in March 2000 with the objective of replacing poorly performing schools. Academies were established and driven by external sponsors, to achieve a transformation in education performance. The Academies Programme was expanded through legislation in the Academies Act 2010. This enables all maintained primary, secondary and special schools to apply to become an Academy. The early focus is on schools rated outstanding by Ofsted and the first of these new academies opened in September 2010. These schools do not have a sponsor but instead are expected to work with underperforming schools to help raise standards.
In Wales, secondary schools take pupils at 11 years old until statutory school age
and beyond.
Ministerial policy is that transfer should be on the basis of nonacademic criteria, however legally post primary schools can still admit pupils based on academic performance.
At the end of this stage of education, pupils are normally entered for a range ofexternal examinations. Most frequently, these are GCSE (General Certificate ofSecondary Education) in England, Wales and Northern Ireland and Standard Gradesin Scotland, although a range of other qualifications are available.
The term public school refers to a group of older, more expensive and exclusive private independent schools in the UK, particularly in -england, which cater primarily for children aged between 13 and 18. Together these schools comprise only around 1% of the total number of schoools in the UK. Traditionally, these were boys´boarding schools, although most now allow day pupils and many have turned either partially or fully co-educationally. They emerged from charity schools established to educate por scholars, the term "public" being used to indicated that Access to them was nos restricted on the basis of religión, occupation, or home location, and that they were subject to public management or control in contrast to private schools which were run for the personal profit of the proprietors

Comentarios
Publicar un comentario